Business Relationship Management is the process which helps the Business Relationship Manager to provide a link between the IT department and the business at strategic and tactical level. The ultimate confirmation that this works is satisfied customers.
Customer refers to the person in the business who has the mandate to decide on and finance the delivery of IT services. This role is usually staffed by a business manager with responsibility for a part of the business.
A condition for this process to function is that the customer role is identified and accepted. In most companies and organizations, the customer role can be identified by following the money. Business line managers with their own budget responsibility where IT is a part of the budget, should be regarded as customers.
Larger organizations sometimes have business line managers without a mandate to influence the content in the IT services. However, such managers can make choices based on existing IT services and have a dialogue about how they can use the services optimally for their operations. This role is defined as purchaser.
One example is a company which determines and finances its IT services at division level. The business department managers within the division are then permitted to conduct their own dialogue with the IT department and order the IT services that are appropriate for their operations. The divisional manager is then the customer and each business line manager is a purchaser.
The reason that these roles are defined differently is that the IT organization should be helped to manage the right question with the right person. For example, a new IT service can be prepared with a purchaser, but for decisions it must be addressed as a business issue to the customer. The objective of identifying customers and purchasers is that these should reflect the business’s existing decision hierarchy.
Purpose
The primary purpose of the process is to understand the business’s need for IT and ensure that the IT services delivered correspond to this need. Furthermore, the aim of the process is to ensure a high level of customer satisfaction. This is achieved through:
- Establishing and maintaining a good relationship with the customer
- Identifying changes in the customer’s operations that can affect the delivery of IT services
- Identifying new technology that can streamline the delivery of IT services to the customer
- Identifying and establishing requirements for new or changed IT services
- Ensuring that the IT delivery meets the business’s requirements
- Agreeing together with the customer on service levels and ensuring that they provide a value for the business
- Establishing a formal route for escalation to the IT steering group
Scope
The process comprises adaptation of the IT organization’s activities based on the business’s objectives. Succeeding in this requires an understanding of:
- Which result the business wants to achieve
- Current range of IT services
- How the customers use IT services
- How IT services are delivered, including service levels and capacity
- Trends within IT which can affect the delivery to the customers
- Level of customer satisfaction and initiative to improve the delivery
- Potential efficiencies for the customer
The above points make it clear that Business Relationship Management has a similar scope to several other processes within the IT department. For example, the connection between the business’s objectives and the IT services that are delivered are a part of the Service Portfolio Management and Service Catalogue Management, which provide existing IT services, and also Management of Service Levels, which comprises agreed and actual service levels.
To avoid creating confusion within the organization, it is important that there is a clear difference between Business Relationship Management and the other processes. The difference is that Business Relationship Management focuses on the customer perspective, and the actual relationship between the IT department and the business, while other processes are focused on the IT services and that they meet the agreed requirements.
Value for the business
The value of Business Relationship Management lies in the fact that the IT organization understands and can describe the business’s requirements for the IT organization. This enables IT to better adapt the delivery of IT services according to the customers’ needs and to provide value for the business.
The process also creates a clear and structured forum for regular communication between IT and the business, which saves time and energy for the business’s customers and purchasers
Activities
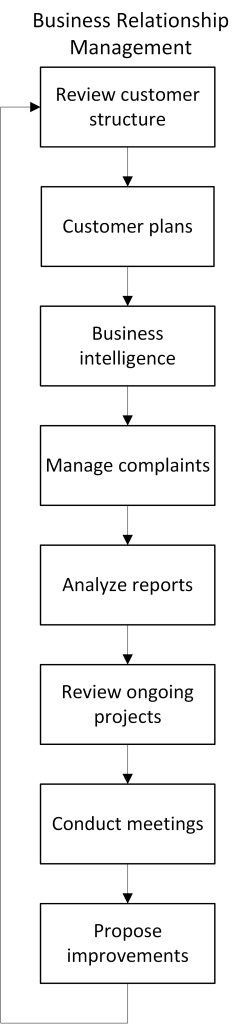
Business Relationship Management is not a process in the sense that the activities have to be followed from start to finish, but it is rather a number of activities that need to be implemented. The activities included are described below in a flow in order to make it structurally simpler, but also as a proposal for a work schedule.
Review the customer structure – Each customer and purchaser should be clearly documented in a common structure. The documentation should be available for everybody within the IT organization and be continually updated.
Go through the customer’s plans – Review and create an understanding for the customer’s operational plan and strategy, as well as related activities, and how this affects the need for IT services.
Business intelligence – Monitor new services and technology which can contribute to making the business more efficient.
Manage complaints – Review and manage complaints and points of view received from customers, purchasers and users.
Analyze reports – Review and analyze reports from other processes within the IT organization in order to create an overall picture of the delivery to the customer. Compile internal reports to be presented to the customer at the next meeting.
Review ongoing projects – Review on-going projects which concern the customer and ensure that these are progressing according to plan.
Meetings – Conduct meetings with customers and purchasers aiming to create and maintain a common plan for the business’s use of IT services.
Propose improvements – Initiate improvement proposals or changes in the service portfolio.
Besides the ongoing activities, there are some activities in the process that are performed at longer intervals, for example, once per year.
Management of agreements – Business Relationship Management is responsible that there is a structured document or a database containing all agreements with the customers. The activity also comprises negotiating and ensuring the financing of the IT delivery with the respective customer.
Measurement of customer satisfaction – Business Relationship Management should measure and follow up customer satisfaction on an ongoing basis. Based on the results, any improvements proposed should be initiated.
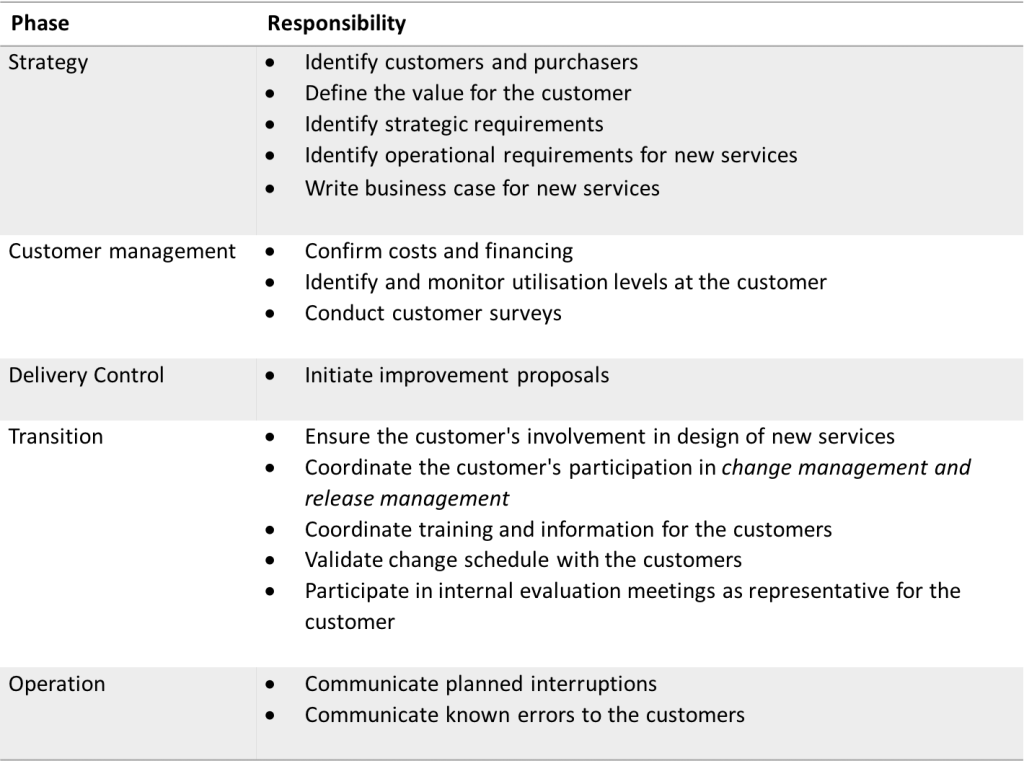
As Business Relationship Management is the single contact point with customers and purchaser, the process has a responsibility to represent them in all other internal processes. The table below shows this responsibility apportioned per phase.
Documentation
All documentation included in Business Relationship Management should be located in the customer database. The documentation is included in the overall knowledge database that is described in the Knowledge Management section.
The following documentation should be located within the framework of Business Relationship Management.
- Contact details for customers and purchasers
- Agreements containing services and levels
- Common procedures
- Minutes from meetings
- Reports
- Customer surveys implemented
Relationships with other processes and functions
Business Relationship Management has links to many other processes. The most common are listed here:

Trigger
The process is triggered through one of the following:
- A strategic initiative in the business
- A new or changed IT service
- An opportunity to make efficiencies
- A change proposed by the business
- A complaint
- When another IT process has an activity that concerns the business
- A customer meeting
- A customer survey should be implemented
- An agreement should be drawn up or revised
Input
The following inputs are needed for the process:
- IT Service strategy
- The business’s strategy
- The service portfolio
- The service catalogue
Output
The following outputs are generated by the process:
- List of customers and purchasers
- Defined value delivered to the business
- Financial agreements with the customers
- Requirements from the customers
- Published results of customer surveys
Measurememnt
This is how the process can be measured:
- Number of customers and purchasers which have a designated contact in the IT department
- Number of customers which have written agreements regarding the delivery
- Results from satisfied customer survey
- The number of complaints from the customers
Challenge
The following elements need specific attention when implementing Business Relationship Management:
- Getting operational managers to understand and staff the customer role
- Creating the capacity to understand and convey the value of IT services in the business
- Creating the possibility of measuring customer satisfaction
- Detecting changes in the customer’s operation that can affect the delivery

